
4、ConcurrentLinkedQueue非阻塞无界链表队列
ConcurrentLinkedQueue是一个线程安全的队列,基于链表结构实现,是一个无界队列,理论上来说队列的长度可以无限扩大。
与其他队列相同,ConcurrentLinkedQueue也采用的是先进先出(FIFO)入队规则,对元素进行排序。 (推荐学习:java面试题目)
当我们向队列中添加元素时,新插入的元素会插入到队列的尾部;而当我们获取一个元素时,它会从队列的头部中取出。
因为ConcurrentLinkedQueue是链表结构,所以当入队时,插入的元素依次向后延伸,形成链表;而出队时,则从链表的第一个元素开始获取,依次递增;
值得注意的是,在使用ConcurrentLinkedQueue时,如果涉及到队列是否为空的判断,切记不可使用size()==0的做法,因为在size()方法中,是通过遍历整个链表来实现的,在队列元素很多的时候,size()方法十分消耗性能和时间,只是单纯的判断队列为空使用isEmpty()即可。
public class ConcurrentLinkedQueueTest { public static int threadCount = 10; public static ConcurrentLinkedQueue<String> queue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<String>(); static class Offer implements Runnable { public void run() { //不建议使用 queue.size()==0,影响效率。可以使用!queue.isEmpty() if (queue.size() == 0) { String ele = new Random().nextInt(Integer.MAX_VALUE) + ""; queue.offer(ele); System.out.println("入队元素为" + ele); } } } static class Poll implements Runnable { public void run() { if (!queue.isEmpty()) { String ele = queue.poll(); System.out.println("出队元素为" + ele); } } } public static void main(String[] agrs) { ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(4); for (int x = 0; x < threadCount; x++) { executorService.submit(new Offer()); executorService.submit(new Poll()); } executorService.shutdown(); }}
一种输出:
入队元素为313732926出队元素为313732926入队元素为812655435出队元素为812655435入队元素为1893079357出队元素为1893079357入队元素为1137820958出队元素为1137820958入队元素为1965962048出队元素为1965962048出队元素为685567162入队元素为685567162出队元素为1441081163入队元素为1441081163出队元素为1627184732入队元素为1627184732
ConcurrentLinkedQuere类图
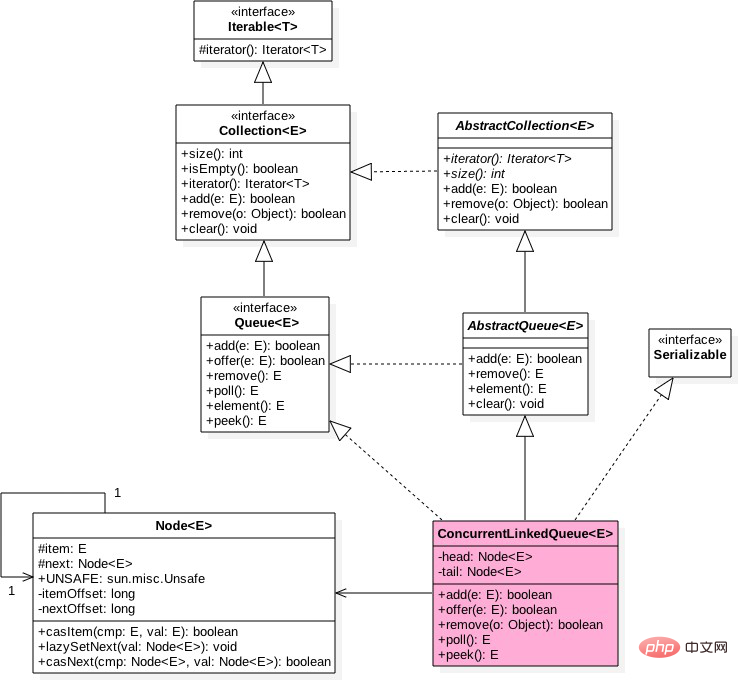
如图ConcurrentLinkedQueue中有两个volatile类型的Node节点分别用来存在列表的首尾节点,其中head节点存放链表第一个item为null的节点,tail则并不是总指向最后一个节点。
Node节点内部则维护一个变量item用来存放节点的值,next用来存放下一个节点,从而链接为一个单向无界列表。
public ConcurrentLinkedQueue(){ head=tail=new Node<E>(null);}
如上代码初始化时候会构建一个 item 为 NULL 的空节点作为链表的首尾节点。
Offer 操作offer 操作是在链表末尾添加一个元素,
下面看看实现原理。
public boolean offer(E e) { //e 为 null 则抛出空指针异常 checkNotNull(e); //构造 Node 节点构造函数内部调用 unsafe.putObject,后面统一讲 final Node<E> newNode = new Node<E>(e); //从尾节点插入 for (Node<E> t = tail, p = t; ; ) { Node<E> q = p.next; //如果 q=null 说明 p 是尾节点则插入 if (q == null) { //cas 插入(1) if (p.casNext(null, newNode)) { //cas 成功说明新增节点已经被放入链表,然后设置当前尾节点(包含 head,1,3,5.。。个节点为尾节点) if (p != t)// hop two nodes at a time casTail(t, newNode); // Failure is OK. return true; } // Lost CAS race to another thread; re-read next } else if (p == q)//(2) //多线程操作时候,由于 poll 时候会把老的 head 变为自引用,然后 head 的 next 变为新 head,所以这里需要 //重新找新的 head,因为新的 head 后面的节点才是激活的节点 p = (t != (t = tail)) ? t : head; else // 寻找尾节点(3) p = (p != t && t != (t = tail)) ? t : q; }}
从构造函数知道一开始有个item为null的哨兵节点,并且head和tail都是指向这个节点。
以上就是java多线程和并发面试题目(第4题,附答案)的详细内容,更多请关注24课堂在线网其它相关文章!






